What Is the New Digital Services Act and How Does It Affect Online Reputation

"The Digital Services Act (DSA) is an EU regulation established to modernize the directive on electronic commerce with regard to illegal content, transparent advertising and disinformation".
Stolton, Samuel (August 18, 2020)
Are you currently operating an online business in Europe, or are you contemplating the prospect of establishing one? If so, this article is poised to capture your attention and provide valuable insights.
The Digital Services Act is a European Union regulation designed to update the e-commerce directive, addressing issues such as illegal content, transparent advertising, and misinformation.
Europe has been looking for ways to regulate tech platforms for a while now. They're doing so through the implementation of the Digital Services Act. Next, we'll tell you what the new Digital Services Act is, its key points, who it affects, and how it influences online reputation.
What Is the New Digital Services Act and Which Companies Does It Affect?
In general terms, this law applies to all online services, but depending on their monthly user count, it will entail additional tasks. The focus is placed on those platforms designated as "very large online platforms," with over 45 million monthly users. In the case of smaller companies, they will have a more extended timeframe to implement the planned changes, which we will discuss shortly.
The European Union conducted a series of assessments beforehand to target the largest platforms. The companies that had to implement the most demanding changes from the outset include AliExpress, Apple AppStore, Bing, Amazon Store, Booking, Facebook, Google Play, Google Maps, Google Search, Google Shopping, LinkedIn, Instagram, Snapchat, Pinterest, TikTok, X, YouTube, Wikipedia, and Zalando.
What Obligations Does It Impose?
To grasp the essence of the new Digital Services Act, we must outline its four pivotal pillars:

- Enhanced User Education
- Greater Protection for Minors
- Vigilant Content Moderation and Reduced Disinformation
- Heightened Transparency and Accountability
In terms of obligations, this law imposes a series of significant restrictions and requirements on tech companies:
- Personalized Advertising: Online advertising based on personal characteristics such as religion, sexual orientation, or ethnic origin is strictly prohibited.
- Dark Patterns Elimination: The practice of using dark patterns is explicitly banned, thereby promoting transparency in online advertising.
- Ease of Unsubscription: The law mandates that unsubscribing from an online service should be as straightforward as signing up, providing users with more effective control over their preferences and personal data.
- Explanations and Right to Appeal: Platforms are obligated to provide detailed explanations when they remove content and must offer tools for users to file complaints in case of disputes.
- Algorithm Transparency: It stipulates that the algorithms used by these platforms must be made public, and users should have the option to choose results not solely based on their personal interests.
The regulation understands that all online services have the goal of combating misinformation, as well as generating transparency reports. To achieve this, the new law regulates aspects such as algorithms, advertising, misinformation, and illicit content.
One of the key points to comprehend the essence of the new Digital Services Act is its prohibition of personalized online advertising based on factors like sexual orientation, religion, or ethnic origin. Additionally, minors are excluded from being targeted. Dark patterns are banned, and unsubscribing must be as simple as subscribing.
Simultaneously, platforms must provide explanations when they remove content and offer tools for their customers to file complaints when such actions occur. Regarding algorithms, they must be made public, and users should have the option to choose a non-interest-based alternative.
Furthermore, platforms now have the obligation to take responsibility for societal risks related to public, physical, and mental health. They must also appoint a responsible individual to oversee law compliance and risk control, subjecting themselves to external audits. To facilitate these analyses, they must provide reports and offer detailed explanations of how their recommendation systems operate.
Additional Obligations
In addition to what was mentioned earlier, those subject to this law must take measures to prevent the dissemination of illegal content while also minimizing adverse impacts on freedom of expression and information. Furthermore, it is required that terms and conditions are consistently clear and upheld.
These platforms must provide mechanisms for users to easily report illicit content, and they must act swiftly upon receiving these notifications. Finally, transparency reports regarding content moderation decisions must be published.
Implementation Timeline
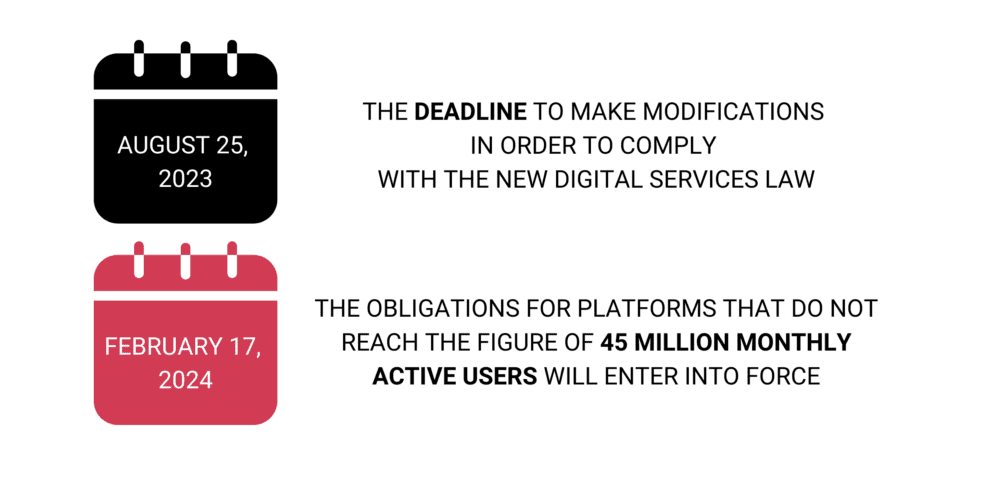
For big tech companies, the deadline to make modifications to comply with the new Digital Services Act was August 25, 2023. However, starting from February 17, 2024, these obligations will come into effect for platforms that do not reach the threshold of 45 million active monthly users. Furthermore, it is also on that date that European Union member states will be required to appoint an individual responsible for coordinating digital services. This person will be responsible for ensuring that the legislation is adhered to.
How the New Digital Services Act Affects Online Reputation
The implementation of the Digital Services Act in the European Union signifies a significant step towards regulating large tech platforms. This legislation directly impacts the digital reputation of companies by establishing stringent obligations to protect individual rights and ensure online transparency. By prohibiting personalized advertising based on personal characteristics and promoting clarity in terms and conditions, the law aims to bolster user trust.
Furthermore, by requiring platforms to promptly address illegal content and provide mechanisms for reporting such content, it reinforces the protection of online freedom of expression and information. However, the real effectiveness of this law in safeguarding online rights remains to be seen. Compliance with these regulations will necessitate significant adjustments on the part of large tech companies. Ultimately, the Digital Services Act seeks to ensure a safer and more secure digital identity for users, and its impact on the online reputation of companies will depend on how well they adapt to and comply with these new regulations.
Conclusion
The implementation of this law requires significant adjustments on the part of major tech companies to meet its objectives. One of the most tangible signs of these changes is the introduction of new forms and reporting channels designed to address content that may infringe upon our individual rights. In essence, this law aims to strengthen the protection of people's digital identity. However, its actual effectiveness is yet to be seen in practice. We will closely monitor its real impact on safeguarding our online rights.
If you want to learn more about the new legislation and its implications for online reputation, at 202 Digital Reputation, we specialize in digital reputation management, taking a 360-degree approach to brand and digital identity protection while helping define and manage our clients' reputation strategies. Contact us to find out more about it.
Read more: What Are the Main Functions of a Reputation Agency





